Feigenbaum-Sharkovskii-Magnitskii (FSM) theory
In all complex nonlinear systems of differential equations describing numerous natural physical, chemical, biological, ecological, and also both economic and social processes and phenomena of a macrocosm, including dissipative and conservative, autonomous and nonautonomous systems, systems of ordinary and partial differential equations and differential equations with delay argument, it is carried out uniform universal bifurcation scenario of complication of dynamics of solutions through the Feigenbaum double period cascade of bifurcations of stable cycles or tori, then through the Sharkovskii subharmonic cascade of bifurcations of births of stable cycles or tori of any period up to the period three according to the Sharkovskii order

Example of the universal scenario of transition to dynamical chaos in two-dimensional nonautonomous systems with periodic coefficients through the subharmonic cascade of bifurcations of stable cycles - generalized Mathieu equation (Fig.1):
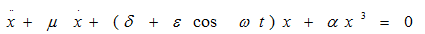
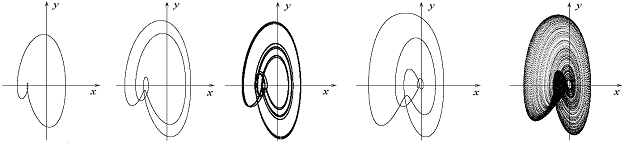
Fig.1. Singular cycle, cycle of period 2, Feigenbaum attractor, cycle of period 3, singular cyclic chaotic attractor in the generalized Mathieu system
Example of the universal scenario of transition to dynamical chaos in autonomous systems through the subharmonic cascade of bifurcations of stable cycles – system of Rossler equations (Fig.2):
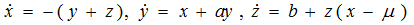
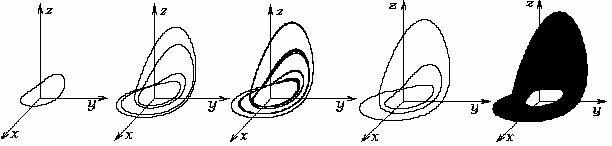
Fig.2. Singular cycle, cycle of period 4, Feigenbaum attractor, cycle of period 3, singular cyclic chaotic attractor in the Rossler system
Example of the universal scenario of transition to dynamical chaos in nonlinear partial differential equations through the subharmonic cascade of bifurcations of stable two-dimensional tori – Kuramoto-Tsuzuki (Ginzburg-Landau) equation (Fig.3):
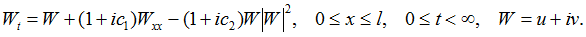
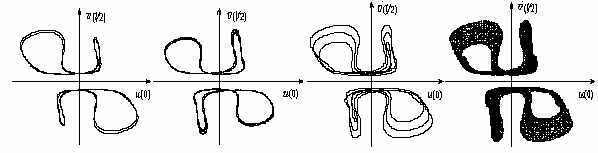
Fig.3. Projections of sections of singular two-dimensional torus of period 2, toroidal Feigenbaum attractor, two-dimensional torus of period 3, singular chaotic toroidal attractor in the K-T (G-L) equation.
Example of the universal scenario of transition to turbulence in Navier-Stokes nonlinear partial differential equations through the subharmonic cascade of bifurcations of stable cycles and stable two-dimensional tori – Rayleigh-Benard convection(Fig.4):
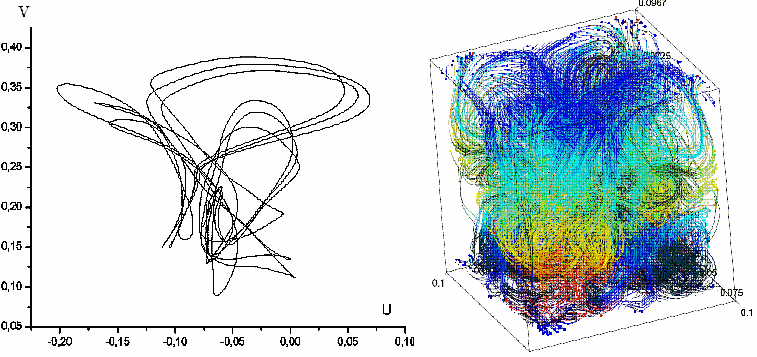
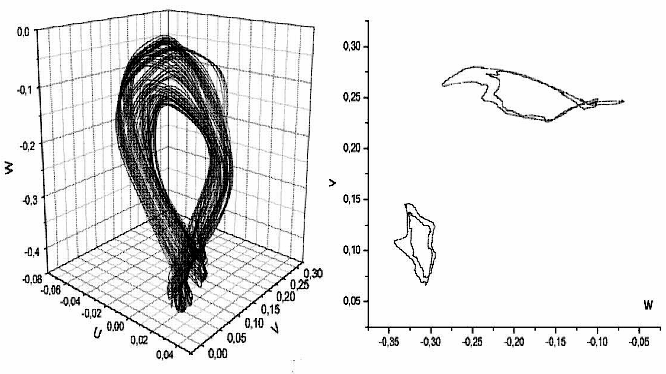
Fig.4. Projections of the cycle of period 3 and real turbulent regime corresponding to him, two-dimensional torus of period 2 and projection of its section
Publications.

Universal Theory of Dynamic and Space-Time Chaos in Complex Systems.
.
Read more
|
Теория динамического хаоса
|
- Nikola Tesla
- Feigenbaum-Sharkovskii-Magnitskii (FSM) theory
- Theory EDCW (electrodynamics of curvilinear waves) of A.Kyriakos
- Electrodynamics of physical vacuum
- Theory of elementary particles
- Gravitation and gravitational waves
- Author: Magnitskii N.A.



